Blood Sugar Levels Chart by Age
Blood Sugar Levels Chart by Age
- What’s ‘normal’ or ‘dangerous’ varies depending on your health status
- Blood Sugar Level Chart Based on Age
- Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart According to Age
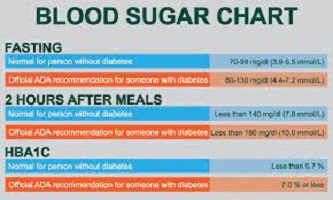
Blood Sugar Levels Chart by Age
The blood sugar levels naturally rise with age, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes in adults in their 50s, 60s, and 70s.
Approximately 27% of those diagnosed with the condition are over the age of 65, which is higher than any other age group. Blood sugar (glucose) objectives for elderly people differ from those for younger ones.
Diabetes management plans are also necessary, particularly for persons diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (usually younger adults) and those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes as they approach the age of 50 or later.
According to one study, the average age for a type 2 diagnosis is 47.9 years.
This article discusses the difficulties of maintaining diabetes as you become older. It discusses blood sugar targets, glucose monitoring, and the advantages of dietary changes and medicines.
What Is Blood Sugar?
The predominant kind of sugar in the body is blood sugar, also known as glucose. It is derived from carbs contained in food.
Glucose is required for the energy supply of cells throughout the body, including brain cells.
As you eat, exercise, and sleep, your blood sugar level swings throughout the day. Stress and hormones are also factors.
People with diabetes should regularly monitor their blood sugar levels to ensure they stay within the right target range, which is generally prescribed by a medical professional.
A blood sugar level that is above the recommended range can have serious health consequences.
“When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can have serious health consequences, such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and heart disease,” explains Brenda Peralta, registered dietitian and certified diabetes educator at FeastGood.com.
According to her, high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can lead to diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can induce confusion, anxiety, weakness, sweating, and vision issues.
Seizures and fainting can occur when blood sugar levels are extremely low.
What is an average blood sugar level?
One of the most important things to deal with for someone living with diabetes is their blood sugar levels.
Have you been diagnosed with this illness?
If you answered yes, you are aware of the everyday problems connected with keeping these levels in check, and how practically everything in your life may revolve around successful sugar control and maintaining a normal glucose level in your blood.
Normal blood sugar levels range from 90 to 110 mg/dL. Every action you take would be accompanied by the thinking “How will this affect my blood sugars?”
” How exhausting must it be when every facet of life, even seemingly unimportant ones like organizing dinners, picnics, and movies, must revolve around regulating blood glucose levels?
Diabetes patients do not have an easy life. Most people, however, are unaware of the underlying conflict.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
A blood glucose level of less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is considered normal. After two hours, blood glucose levels of more than 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) suggest diabetes. Prediabetes is defined as blood sugar levels ranging from 140 to 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L to 11.0 mmol/L).
What is blood glucose?
Blood glucose is a type of sugar found in the blood. This sugar originates from the food we eat and is our bodies’ primary source of energy. In addition, glucose can be produced in the body and stored for later use. The blood transports this glucose to all of the cells in the body, where it is used for energy.
If there is too much glucose in the blood, it can lead to major health problems over time. Even if you are not diabetic, problems can emerge if your blood sugar level is too low or too high.
How do blood sugar levels differ with age?
Blood sugar levels vary with age, and different age groups may have different goal levels for blood sugar regulation. Here’s how blood sugar levels differ with age:
1. Because of their smaller body size and higher activity levels, children often have lower blood sugar levels than adults.
Hormones might cause blood sugar levels to vary more frequently during adolescence. This can make controlling blood sugar levels more difficult and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
2. Blood sugar levels in people tend to rise with age. This is attributable in part to metabolic changes and a decrease in physical activity levels. However, blood sugar levels in adults might vary depending on their lifestyle, genetics, and other health concerns.
3. Blood sugar levels in seniors may become more difficult to maintain as a result of age-related changes in the body, such as decreasing insulin sensitivity and muscle mass.
It is crucial to note that blood sugar levels might change depending on the time of day, if you have recently eaten, and other factors. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels can help uncover potential health issues and boost general health and well-being.

A blood sugar level chart is a tool for tracking blood sugar levels over time. It often encompasses a range of normal blood sugar levels as well as those that may suggest a potential health risk.
If your blood sugar level rises or falls outside of the normal range, it could be a symptom of an illness such as diabetes or hypoglycemia. These are severe medical disorders that might cause serious harm if therapy is not started as soon as possible.
Thus, understanding the typical blood sugar levels chart by age is critical to constantly monitor the differences. Continue reading to obtain a better understanding of the chart.
Blood Sugar Levels for Children
While blood sugar issues are more common in adults, it is critical to maintain an average blood sugar level in children as well. To avoid health concerns, children aged 6 to 12 years should keep their blood sugar levels regular.
| Situation | Blood Sugar Level |
| Fasting | 80 to 180 mg/dL |
| Before meals | 90 to 180 mg/dL |
| 1-2 hours post meals | Up to 140 mg/dL |
| Before bedtime | 100 to 180 mg/dL |
Blood Sugar Levels for Teenagers
Unless a teenager has diabetes, there is no universally accepted guideline for the appropriate blood glucose level for teenagers.
However, the table below might provide you with a rudimentary grasp of the appropriate blood sugar level for teenagers.
The usual blood sugar levels for teenagers aged 13 to 19 years are as follows;
| Situation | Blood Sugar Level |
| Fasting | 70 to 150 mg/dL |
| Before meals | 90 to 130 mg/dL |
| 1 to 2 hours post meals | Up to 140 mg/dL |
| Before bedtime | 90 to 150 mg/dL |
Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
Adults above the age of 20 are particularly vulnerable to the hazards of diabetes.
The table below provides information about normal blood sugar levels for persons aged 25 to 60.
Blood Sugar Levels in Seniors (Older Adults)
Persons over the age of 65 have a worse ability to maintain optimal glucose levels than younger persons.
Diabetes and associated comorbidities, such as renal disease, retinopathy, and neuropathy, are likely to cause substantial variations in blood glucose levels in such elderly persons.
Their health will be determined by the extent of injury to the pancreas. Here’s a chart of blood sugar levels by age 70;
| Blood Sugar Levels in Older Adults Age 50 and Above | |||
| Level | 0-2 hours after a meal | 2-4 hours after a meal | 4-8 hours after a meal |
| Dangerously high | Over 300 mg/dL | Over 200 mg/dL | +180 mg/dL |
| High | 140-220 mg/dL | 130-220 mg/dL | 120-180 mg/dL |
| Normal | 90-140 mg/dL | 90-130 mg/dL | 80-120 mg/dL |
| Low | 80-90 mg/dL | 70-90 mg/dL | 60-80 mg/dL |
| Dangerously low | 0-80 mg/dL | 0-70 mg/dL | 0-60 mg/dL |
Why Is Blood Sugar Important in Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition in which the body’s ability to regulate glucose levels on its own becomes difficult or impossible.
When someone has diabetes, their body is either unable to create enough insulin or is unable to make enough insulin available for use.
Insulin is a hormone that aids the body’s utilization of glucose for energy. When insulin levels are excessively low, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, causing organ and tissue damage.
“Diabetes occurs when a person’s body is unable to adequately manage sugar that is consumed normally in our everyday diet,” says Jennifer Meller, M.D., chief medical officer at Sweetch, a Tel Aviv, Israel-based digital health care innovation company.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar
“Chronically elevated blood sugar levels can lead to changes in both large and small blood vessels.”
Dr. Meller says that changes to major vessels can raise the risk of heart attack and stroke over time, but damage to small veins can cause nerve damage, eyesight loss, and renal failure.
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is critical for diabetics to avoid major health concerns in the future. This necessitates establishing target glucose levels for different age groups and implementing lifestyle changes accordingly, as blood sugar levels might fluctuate depending on what and when you consume, among other factors.
What Is an A1C Number?
An A1C test, also known as glycosylated hemoglobin, is a common diagnostic tool for determining a person’s average blood sugar levels during the previous three months (90 days).
It demonstrates how successfully you managed your blood sugar throughout that period.
“It’s an important measure of blood sugar control in diabetes because it provides a long-term view of blood sugar levels and can help predict the risk of diabetic complications,” Peralta says.

Age is only one element that can affect glucose levels. Blood sugar targets for children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly may differ.
The clinical guidelines for various age groups are detailed in the chart above.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Now that you understand the ages 40, 50, and 70 sugar level chart, you may want to learn more about the causes of blood sugar swings.
A variety of things influence your blood sugar levels, both positively and negatively. Here is a list of them for your convenience:
- Hydration levels
- Medicines
- Medication dosage error
- Stress
- Food selection and physical activity
Tips for Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
If you believe you may have blood sugar variations after seeing the age-based sugar level chart, here are a few ideas to help you maintain an average blood sugar level.
- With frequent blood sugar testing, you can keep track of your blood sugar levels.
- Make physical activities and exercises a part of your everyday routine.
- Stay hydrated by drinking more water.
- Develop a high-fiber diet and avoid foods heavy in saturated and trans-fat, sugar, salt, and calories.
- Limit your alcohol consumption.
- Control your food portions to guarantee a healthy dinner.
- Fruits should be preferred over sweet desserts and sweet foods.
- Avoid skipping any meals and stick to a regular eating schedule.
How to Monitor Your Blood Sugar
Your doctor will advise you how frequently you should check your blood sugar at home. There are numerous methods for checking blood sugar at home.
You can check your blood sugar with a blood glucose monitor. A finger stick instrument (called a lancing device) is used in this approach to get a drop of blood.
Then, a drop of blood is placed on a test strip, which is then inserted into the monitor. The monitor will then provide you with a blood sugar reading.
FAQs
What is the normal blood sugar according to age?
Adults should have levels ranging from 90 to 130 mg/dL (5.0 to 7.2 mmol/L). For children aged 13 to 19, the range is 90 to 130 mg/dL (5.0 to 7.2 mmol/L).
Children aged between 6 to 12, the range is 90 to 180 mg/dL (5.0 to 10.0 mmol/L). For children under the age of six, the range is 100 to 180 mg/dL (5.5 to 10.0 mmol/L).
What constitutes a healthy blood sugar level in the morning?
According to doctors, a typical fasting blood sugar range is 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.6 mmol/L).
Your doctor will diagnose diabetes if your fasting blood sugar regularly exceeds 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L).
You can lower your chances of having high fasting blood sugar by eating dinner earlier the night before.
How much blood sugar is considered normal for adults?
Fasting blood sugar levels of less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) are considered normal. Prediabetes is defined as fasting blood sugar levels ranging from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L).
Diabetes is diagnosed when your blood sugar level is 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or greater on two different tests.
What is the usual blood sugar level for a 40-year-old female after a meal?
Adults with normal glucose metabolism should keep their blood glucose levels below 140 mg/dL after meals, according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF).
Healthy persons with normal glucose tolerance have been reported to keep their blood glucose levels below 140 mg/dL 95-99 percent of the time.
How can I keep my blood sugar under control at the age of 40?
12 Natural Ways to Lower Blood Sugar
- Walk It Out.
- Eat More Barley.
- Bump Up Your Exercise Intensity.
- Pick Veggies Wisely.
- Get Enough Vitamin D.
- Combine Your Macronutrients.
- Go for Whole Fruit over Juice.
- Walk After Meals.
What should a female blood sugar level be after eating?
According to clinical guidelines from diabetes experts and other medical professionals, your glucose levels should be between 140 and 180 mg/dL after eating.
What should a woman’s blood sugar level be after eating?
What Is a Healthy Blood Sugar Level? They’re less than 100 mg/dL after at least 8 hours of not eating (fasting). And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours later.
What is the amount of sugar in 40 years old?
What constitutes high blood sugar in a person in their forties?
If a 40-year-old person’s blood sugar level surpasses 130 mg/dL, he or she may have high blood sugar levels. This could be a significant health risk for them and should be closely monitored.
What should your blood sugar level be two hours after eating?
A blood sugar target is a range that you strive to stay within as much as feasible. These are normal targets: 80 to 130 mg/dL before a meal. Less than 180 mg/dL two hours after the start of a meal.
What time of day is blood sugar highest?
The dawn phenomenon causes elevated blood sugar levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia.
It usually occurs between 4 a.m. and 8 a.m. The origin of the dawn phenomena is unknown.
Some researchers believe that the natural nighttime release of some hormones enhances insulin resistance.
What blood sugar level is considered dangerous?
What blood sugar level is considered dangerous? Sugar levels above 250 mg/dL are considered extremely high.
However, blood sugar levels beyond 300 mg/dL can be hazardous. If your blood sugar levels are higher than 300 mg/dL in two consecutive measurements, see your doctor right away.
Blood sugar levels between the ages of 50 and 60
Normal readings are 0-50 years – < 140 mg/dL or < 7.8 mmol/L (SI units) 50-60 years – < 150 mg/dL. 60 years and older – < 160 mg/dL.
Chart of normal blood sugar levels
Blood sugar levels are used to diagnose diabetes.
| Plasma glucose test | Normal | Prediabetes |
| Random | Below 11.1 mmol/l Below 200 mg/dl | N/A |
| Fasting | Below 5.5 mmol/l Below 100 mg/dl | 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l 100 to 125 mg/dl |
| 2 hour post-prandial | Below 7.8 mmol/l Below 140 mg/dl | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l 140 to 199 mg/dl |
Normal blood sugar levels for adults
What Is a Healthy Blood Sugar Level?
They’re less than 100 mg/dL after at least 8 hours of not eating (fasting). And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours later.
During the day, levels are typically lowest soon before meals.
Sugar level normal range
What is an average blood glucose level? Without diabetes, a healthy (normal) fasting blood glucose level is 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L).
Values between 50 and 70 mg/dL (2.8 to 3.9 mmol/L) can also be considered “normal” in those who do not have diabetes.
Normal blood sugar levels chart for adults without diabetes
Normal Blood Sugar Levels by Age (Children, Adults, and Seniors)
| Age | Normal Fasting Glucose (without diabetes) | Target Glucose Range (before meals for those with type 2 diabetes) |
| Adults | Less than or equal to 100mg/dL | 80 to 130mg/dL |
| Older adults | Less than or equal to 100mg/dL | 80 to 150 or 170mg/dL |
Blood sugar levels after eating
What Is a Healthy Blood Sugar Level? They’re less than 100 mg/dL after at least 8 hours of not eating (fasting).
And they’re less than 140 mg/dL two hours later. During the day, levels are typically lowest soon before meals.
Random blood sugar normal range
If you had a fasting blood glucose test, a level of 70 to 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L) is considered normal.
A normal result from a random blood glucose test is dependent on when you last ate. The blood glucose level will usually be 125 mg/dL (6.9 mmol/L) or below.


